Tire Size and What It Means - Complete Guide to Understanding Tire Codes
Understanding tire size codes is essential for proper tire selection, vehicle safety, and performance optimization. This comprehensive guide explains the meaning behind every number and letter in tire size codes.
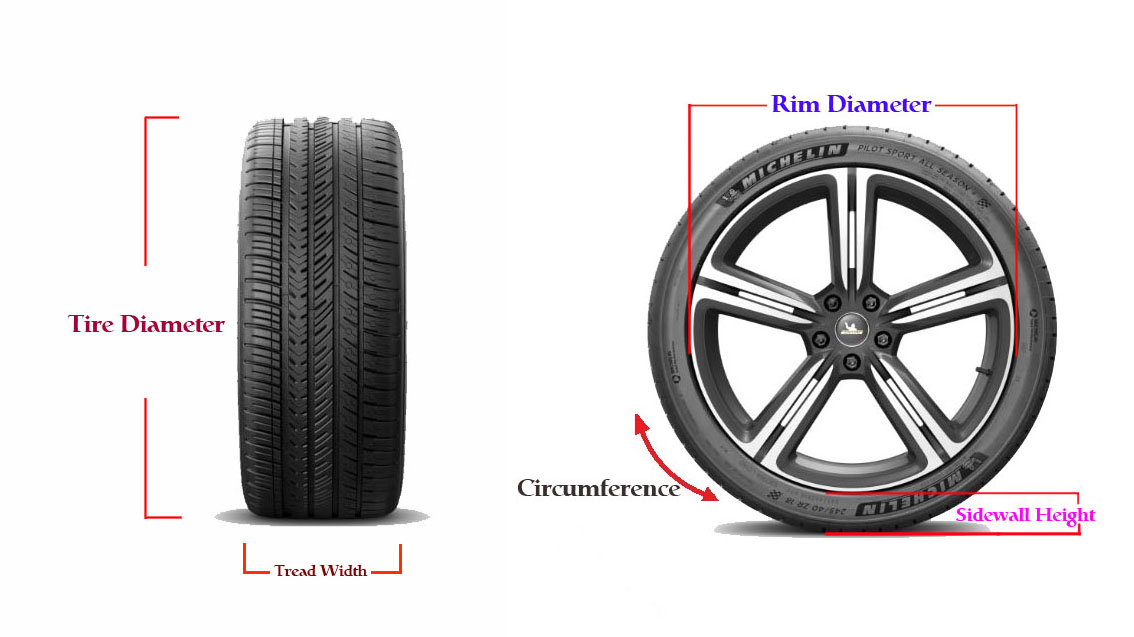
Understanding tire size codes helps you make informed decisions about tire selection and vehicle compatibility.
What is a Tire Size Code?
A tire size code is a standardized alphanumeric sequence that provides detailed information about a tire's physical dimensions, construction type, load capacity, and speed capabilities. This code appears on the tire's sidewall and follows an internationally recognized format.
Standard Tire Size Format
205/65R16 95H
Each part of this code represents specific tire characteristics
Breaking Down Tire Size Components
205 - Section Width
- What it means: The width of the tire from sidewall to sidewall
- Unit: Millimeters
- Measurement: Taken when mounted on recommended rim width and properly inflated
- Example: 205 mm = 8.07 inches
- Impact: Affects traction, fuel economy, and handling
65 - Aspect Ratio
- What it means: The height of the sidewall as a percentage of the section width
- Calculation: Sidewall height = Section width × (Aspect ratio ÷ 100)
- Example: 205 × (65 ÷ 100) = 133.25 mm (5.25 inches)
- Purpose: Determines ride comfort and handling characteristics
- Impact: Lower numbers = sportier, higher numbers = more comfort
R - Construction Type
- R: Radial construction (most common)
- D: Diagonal/Bias ply construction (older style)
- B: Belted bias construction
- Radial tires: Offer better performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity
- Benefits: Improved handling, longer tread life, better fuel economy
16 - Rim Diameter
- What it means: The diameter of the wheel rim the tire fits
- Unit: Inches
- Important: Must match your wheel size exactly
- Example: 16-inch wheels require 16-inch tires
- Impact: Affects overall tire diameter and speedometer accuracy
Load and Speed Ratings
95 - Load Rating
- What it means: Maximum load capacity the tire can carry
- Scale: 60-150 (higher numbers = higher capacity)
- Example: 95 = 1,521 lbs per tire
- Total: 4 tires × 1,521 lbs = 6,084 lbs total capacity
- Safety: Never exceed load rating for vehicle safety
H - Speed Rating
- What it means: Maximum speed the tire can safely handle
- Scale: L-Z (higher letters = higher speeds)
- Example: H = 130 mph maximum
- Important: Never exceed speed rating for safety
- Performance: Higher ratings = better performance but higher cost
Visual Examples
Example 1: 195/65R15 91H
195: 7.68 inches wide
65: Sidewall is 65% of width (4.99 inches tall)
R: Radial construction
15: Fits 15-inch wheels
91: Can carry 1,323 lbs per tire
H: Safe up to 130 mph
Typical Use: Compact cars, daily commuting
Performance: Balanced comfort and efficiency
Example 2: 245/40R18 97W
245: 9.65 inches wide
40: Sidewall is 40% of width (3.86 inches tall)
R: Radial construction
18: Fits 18-inch wheels
97: Can carry 1,609 lbs per tire
W: Safe up to 168 mph
Typical Use: Performance cars, sports sedans
Performance: Sporty handling, high-speed capability
Example 3: 265/70R17 115S
265: 10.43 inches wide
70: Sidewall is 70% of width (7.30 inches tall)
R: Radial construction
17: Fits 17-inch wheels
115: Can carry 2,679 lbs per tire
S: Safe up to 112 mph
Typical Use: SUVs, trucks, off-road vehicles
Performance: High load capacity, off-road capability
Understanding the Impact of Each Component
Section Width Impact
- Wider tires: Better grip and handling
- Narrower tires: Better fuel efficiency
- Performance: Wider = better cornering
- Economy: Narrower = lower rolling resistance
Aspect Ratio Impact
- Lower ratios: Sportier handling
- Higher ratios: More comfortable ride
- Ground clearance: Higher = more clearance
- Appearance: Lower = more aggressive look
Rim Diameter Impact
- Larger rims: Better handling
- Smaller rims: More comfortable ride
- Speedometer: Affects accuracy
- Appearance: Larger = more modern look
Load Rating Impact
- Higher ratings: More capacity
- Safety margin: Important for heavy loads
- Towing: Consider additional weight
- Durability: Higher ratings = stronger construction
Speed Rating Impact
- Higher ratings: Better performance
- Safety: Never exceed rating
- Cost: Higher ratings = higher cost
- Handling: Better at high speeds
Construction Impact
- Radial: Better performance
- Fuel efficiency: Lower rolling resistance
- Longevity: Longer tread life
- Handling: Improved responsiveness
Common Misconceptions About Tire Sizes
❌ Bigger is Always Better
While larger tires may look more impressive, they can negatively impact fuel economy, ride comfort, and vehicle performance if not properly matched to your vehicle's specifications.
❌ All Tires Are the Same
Tire sizes are not interchangeable. Each component of the tire size code serves a specific purpose and must be matched to your vehicle's requirements.
❌ Speed Rating Doesn't Matter
Speed ratings are crucial for safety. Exceeding the speed rating can lead to tire failure, especially at high speeds.
✅ Proper Matching is Essential
Always consult your vehicle's owner's manual and ensure all tire specifications match the manufacturer's recommendations for optimal performance and safety.
Professional Recommendations
Tire Selection Tips
- •Check Owner's Manual: Always verify recommended tire sizes
- •Consider Climate: Choose appropriate tires for your climate
- •Match Load Rating: Ensure tires can handle vehicle weight
- •Verify Speed Rating: Match to vehicle capabilities
Safety Considerations
- •Never Exceed: Load or speed ratings
- •Proper Inflation: Maintain recommended pressure
- •Regular Inspection: Check for wear and damage
- •Professional Installation: Use qualified technicians
Ready to Understand Your Tire Size?
Use our interactive tire size calculator to analyze your current tires and find compatible alternatives.