Tire Size What It Means - Complete Guide to Understanding Tire Codes
Tire Size What It Means - Complete Guide to Understanding Tire Codes
Understanding tire size codes is essential for proper tire selection, maintenance, and vehicle safety. This comprehensive guide explains what each number and letter in a tire size means and how to interpret tire specifications.
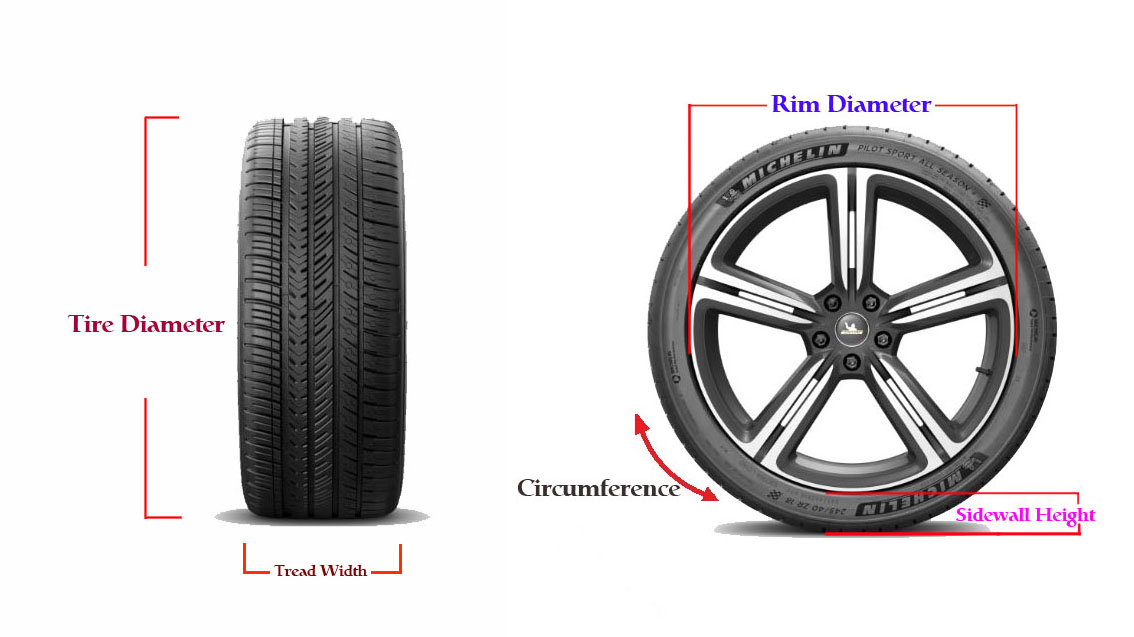
Understanding tire size codes helps you make informed decisions about tire selection and maintenance.
What is a Tire Size?
A tire size is a standardized code that provides detailed information about a tire's dimensions, construction, and performance capabilities. This code appears on the tire's sidewall and follows a specific format that manufacturers worldwide use.
Example: 205/65R16 95H
Let's break down this common tire size code:
Breaking Down the Tire Size Code
205 - Section Width
- What it means: The width of the tire from sidewall to sidewall
- Unit: Millimeters
- Measurement: Taken when mounted on recommended rim width and properly inflated
- Example: 205 mm = 8.07 inches
65 - Aspect Ratio
- What it means: The height of the sidewall as a percentage of the section width
- Calculation: Sidewall height = Section width × (Aspect ratio ÷ 100)
- Example: 205 × (65 ÷ 100) = 133.25 mm (5.25 inches)
- Purpose: Determines ride comfort and handling characteristics
R - Construction Type
- R: Radial construction (most common)
- D: Diagonal/Bias ply construction (older style)
- B: Belted bias construction
- Radial tires: Offer better performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity
16 - Rim Diameter
- What it means: The diameter of the wheel rim the tire fits
- Unit: Inches
- Important: Must match your wheel size exactly
- Example: 16-inch wheels require 16-inch tires
95 - Load Rating
- What it means: Maximum load capacity the tire can carry
- Scale: 60-150 (higher numbers = higher capacity)
- Example: 95 = 1,521 lbs per tire
- Total: 4 tires × 1,521 lbs = 6,084 lbs total capacity
H - Speed Rating
- What it means: Maximum speed the tire can safely handle
- Scale: L-Z (higher letters = higher speeds)
- Example: H = 130 mph maximum
- Important: Never exceed speed rating for safety
Complete Tire Size Format
Standard Format: XXX/XXRXX XXX X
Example: 225/45R17 91V
- 225: Section width in millimeters
- 45: Aspect ratio (percentage)
- R: Radial construction
- 17: Rim diameter in inches
- 91: Load rating
- V: Speed rating
Understanding Each Component
Section Width (First Number)
The section width affects:
- Traction: Wider tires generally provide better grip
- Fuel Economy: Narrower tires are more fuel-efficient
- Handling: Wider tires improve cornering stability
- Comfort: Width affects ride quality
Common Widths:
- 185-195: Compact cars
- 205-215: Small sedans
- 225-235: Midsize sedans
- 245-255: Large sedans and SUVs
- 265-275: Performance cars
- 285+: High-performance and luxury vehicles
Aspect Ratio (Second Number)
The aspect ratio determines:
- Ride Comfort: Higher ratios = more cushion
- Handling: Lower ratios = sportier handling
- Ground Clearance: Higher ratios = more clearance
- Appearance: Lower ratios = more aggressive look
Common Ratios:
- 30-40: Ultra-low profile (sport cars)
- 45-50: Low profile (performance cars)
- 55-60: Standard (most passenger cars)
- 65-70: High profile (trucks, SUVs)
- 75+: Extra high profile (off-road vehicles)
Construction Type (Letter)
R - Radial (Most Common):
- Steel belts run radially across the tire
- Better performance and fuel efficiency
- Longer tread life
- Improved handling
D - Diagonal/Bias Ply:
- Older construction method
- Less common in modern vehicles
- Used in some specialty applications
Rim Diameter (Number)
Important Considerations:
- Must match wheel size exactly
- Affects overall tire diameter
- Impacts speedometer accuracy
- Influences vehicle appearance
Common Sizes:
- 14-15: Small cars
- 16-17: Most passenger cars
- 18-19: Performance and luxury cars
- 20+: High-end vehicles
Load Rating Chart
| Rating | Load Capacity (lbs) | Rating | Load Capacity (lbs) | |--------|-------------------|--------|-------------------| | 60 | 551 | 85 | 1,135 | | 65 | 639 | 90 | 1,323 | | 70 | 739 | 95 | 1,521 | | 75 | 853 | 100 | 1,764 | | 80 | 992 | 105 | 2,039 |
Speed Rating Chart
| Rating | Max Speed (mph) | Rating | Max Speed (mph) | |--------|----------------|--------|----------------| | L | 75 | S | 112 | | M | 81 | T | 118 | | N | 87 | U | 124 | | P | 93 | H | 130 | | Q | 99 | V | 149 | | R | 106 | W | 168 | | Z | 149+ | Y | 186 |
How to Read Your Tire Size
Step 1: Find the Tire Size Code
Look on the tire's sidewall for a series of numbers and letters like: P205/65R16 95H
Step 2: Break Down Each Component
- P: Passenger car tire (optional prefix)
- 205: Section width in millimeters
- 65: Aspect ratio
- R: Radial construction
- 16: Rim diameter in inches
- 95: Load rating
- H: Speed rating
Step 3: Understand What Each Means
- Width: How wide the tire is
- Aspect Ratio: How tall the sidewall is
- Construction: How the tire is built
- Diameter: What size wheel it fits
- Load: How much weight it can carry
- Speed: How fast it can safely go
Tire Size Examples Explained
Example 1: 195/65R15 91H
- 195: 7.68 inches wide
- 65: Sidewall is 65% of width (4.99 inches tall)
- R: Radial construction
- 15: Fits 15-inch wheels
- 91: Can carry 1,323 lbs per tire
- H: Safe up to 130 mph
Example 2: 245/40R18 97W
- 245: 9.65 inches wide
- 40: Sidewall is 40% of width (3.86 inches tall)
- R: Radial construction
- 18: Fits 18-inch wheels
- 97: Can carry 1,609 lbs per tire
- W: Safe up to 168 mph
Example 3: 265/70R17 115S
- 265: 10.43 inches wide
- 70: Sidewall is 70% of width (7.30 inches tall)
- R: Radial construction
- 17: Fits 17-inch wheels
- 115: Can carry 2,679 lbs per tire
- S: Safe up to 112 mph
Important Considerations
Vehicle Compatibility
- Check Owner's Manual: Always verify recommended tire sizes
- OEM Specifications: Use original equipment sizes when possible
- Clearance: Ensure adequate wheel well clearance
- Suspension: Consider suspension modifications
Performance Impact
- Wider Tires: Better grip, higher fuel consumption
- Lower Aspect Ratio: Sportier handling, less comfort
- Higher Load Rating: More capacity, stiffer ride
- Higher Speed Rating: Better performance, higher cost
Safety Considerations
- Never Exceed: Load or speed ratings
- Match Ratings: Ensure tires meet vehicle requirements
- Proper Inflation: Maintain recommended pressure
- Regular Inspection: Check for wear and damage
Common Tire Size Categories
Passenger Car Tires
- Typical Sizes: 185/65R15 to 245/45R18
- Load Ratings: 80-100
- Speed Ratings: S-V
- Applications: Daily driving, commuting
Performance Tires
- Typical Sizes: 225/40R18 to 295/35R20
- Load Ratings: 90-110
- Speed Ratings: V-Z
- Applications: Sports cars, high-performance vehicles
SUV/Truck Tires
- Typical Sizes: 235/75R16 to 285/70R17
- Load Ratings: 100-120
- Speed Ratings: S-T
- Applications: SUVs, trucks, off-road vehicles
Winter Tires
- Typical Sizes: Same as summer tires
- Special Features: Winter compound, tread design
- Applications: Cold weather, snow, ice
Tire Size Calculator Usage
Using Our Calculator
- Enter Current Size: Input your current tire size
- View Measurements: See width, height, diameter in both units
- Compare Sizes: Compare with alternative sizes
- Check Compatibility: Verify fitment with your vehicle
Benefits of Understanding Tire Sizes
- Better Selection: Choose appropriate tires for your needs
- Improved Safety: Ensure proper load and speed ratings
- Cost Savings: Avoid incompatible tire purchases
- Performance: Optimize handling and comfort
Professional Recommendations
Tire Shop Consultation
- Expert Advice: Professional fitment recommendations
- Vehicle-Specific: Tailored to your vehicle and driving needs
- Safety First: Priority on safety and compatibility
- Performance: Balance performance with practicality
Regular Maintenance
- Monthly Checks: Pressure and condition
- Quarterly Service: Rotation and balance
- Annual Inspection: Comprehensive evaluation
- Professional Installation: Proper mounting and balancing
For more information about tire sizes and calculations, visit our tire size calculator and tire pressure calculator.
Published: December 19, 2024